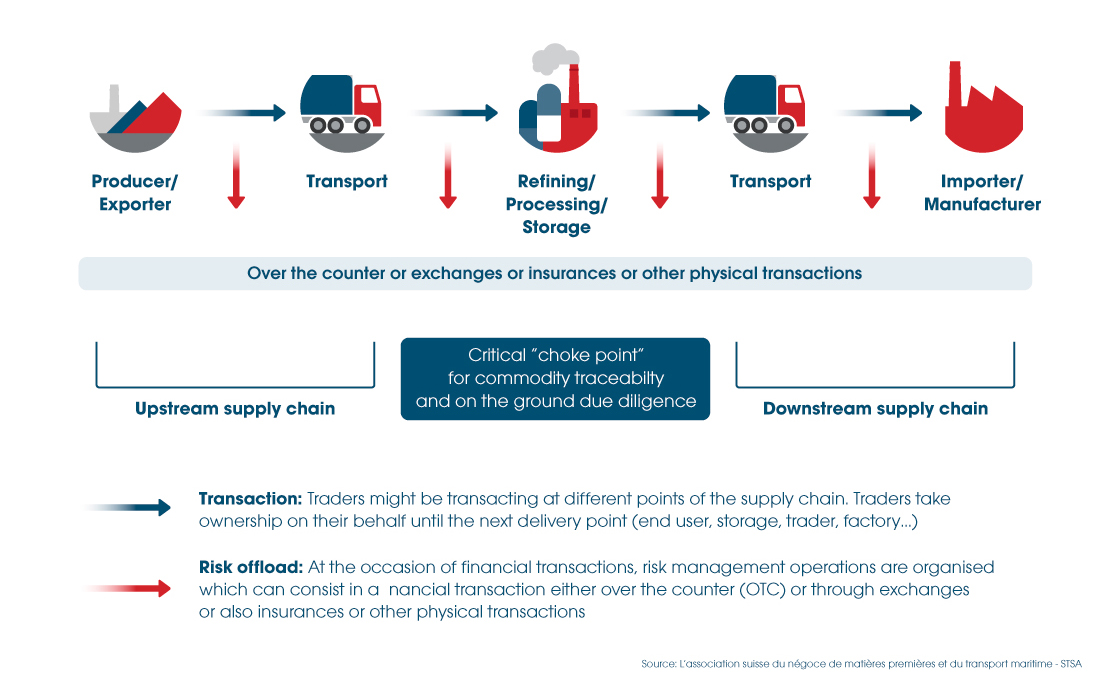
Commodity chains are the invisible threads that connect the world, binding producers, suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers into a seamless web of global commerce. Imagine a world without these chains—where raw materials don’t reach factories, and finished goods don’t make it to store shelves. Sounds chaotic, right? Well, that’s why understanding commodity chains is crucial for anyone interested in economics, business, or even just staying informed about how the world works. So, buckle up as we dive deep into the fascinating world of commodity chains and uncover their secrets.
Think of commodity chains as the unsung heroes of globalization. They’re responsible for turning raw materials like cocoa beans, crude oil, or cotton into the chocolate bars, gasoline, and T-shirts we use every day. But what exactly are they? Simply put, a commodity chain is the sequence of activities involved in transforming raw materials into finished products that end up in the hands of consumers. From mining to manufacturing, shipping to retail, every step in this chain plays a vital role in the global economy.
Now, you might be wondering why you should care about commodity chains. Well, here’s the thing—they impact everything from the price of your morning coffee to the availability of the latest smartphone. By understanding how these chains work, you can better grasp the complexities of global trade, identify potential disruptions, and even spot opportunities for innovation. So, whether you’re a business owner, a student, or just a curious mind, this article will give you the inside scoop on commodity chains and their role in shaping our world.
Read also:Kotaro Lives Alone Season 2 The Epic Return Of Japans Favorite Lonely Hero
What Exactly is a Commodity Chain?
Let’s break it down. A commodity chain is essentially the series of processes and activities that take a product from its raw form to its final state. It’s like a relay race where each participant has a specific role to play. The chain typically starts with extraction or production of raw materials, moves through processing and manufacturing, and ends with distribution and consumption. But it’s not as simple as it sounds. Each link in the chain is interconnected, and a disruption in one part can have ripple effects throughout the entire system.
For instance, if there’s a shortage of coffee beans due to poor harvests in major producing countries, it could lead to higher prices at your local café. Or if there’s a disruption in shipping lanes, it could delay the delivery of electronics to retailers. These examples highlight the importance of understanding the intricacies of commodity chains and how they influence the goods and services we rely on daily.
The Key Players in a Commodity Chain
Every successful commodity chain involves a variety of players, each with their own responsibilities. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Producers: These are the farmers, miners, or fishermen who extract or produce raw materials.
- Suppliers: They provide the necessary inputs, such as machinery, tools, or technology, to producers and manufacturers.
- Manufacturers: These guys turn raw materials into finished products through processing and assembly.
- Distributors: Responsible for getting the products from manufacturers to retailers or directly to consumers.
- Consumers: The end-users who purchase and use the final products.
Each of these players has their own challenges and opportunities, and their interactions shape the efficiency and effectiveness of the commodity chain. For example, a producer might focus on increasing yields, while a distributor might prioritize reducing transportation costs. Understanding these dynamics can help businesses optimize their operations and improve their bottom line.
Types of Commodity Chains
Not all commodity chains are created equal. Depending on the product and industry, they can vary significantly in structure and complexity. Here are some common types:
1. Agricultural Commodity Chains
These chains focus on agricultural products like grains, fruits, vegetables, and livestock. They typically involve farmers, processors, and distributors. For example, the wheat commodity chain starts with farmers growing wheat, moves through milling and baking, and ends with bread on supermarket shelves.
Read also:Emily Balkind Engaged The Inside Scoop On Love Life And Everything In Between
2. Industrial Commodity Chains
These chains deal with manufactured goods like electronics, automobiles, and textiles. They often involve multiple stages of production and assembly. Think about the smartphone you’re using right now—it’s likely the result of a complex industrial commodity chain involving chip manufacturers, assembly plants, and logistics companies.
3. Energy Commodity Chains
From oil and gas to renewable energy sources like wind and solar, energy commodity chains are critical for powering our world. They involve extraction, refining, and distribution processes that ensure energy is available to households and industries worldwide.
How Commodity Chains Impact Global Trade
Commodity chains are the lifeblood of global trade, facilitating the movement of goods across borders and continents. They enable countries to specialize in producing what they’re best at and trading for what they need. For example, a country rich in cocoa beans might export them to chocolate manufacturers in Europe, while importing electronics from Asia.
However, global trade isn’t without its challenges. Tariffs, trade wars, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt commodity chains, leading to higher prices and shortages. That’s why businesses and governments must work together to ensure the smooth functioning of these chains and minimize potential disruptions.
The Role of Technology in Commodity Chains
Technology has revolutionized commodity chains, making them more efficient and transparent. Innovations like blockchain, IoT, and AI are transforming how goods are tracked, managed, and delivered. For instance, blockchain can provide a tamper-proof record of every step in a commodity chain, ensuring accountability and reducing fraud. Meanwhile, AI-powered analytics can help predict demand and optimize inventory levels, reducing waste and costs.
Challenges Facing Commodity Chains
Despite their importance, commodity chains face numerous challenges that can impact their effectiveness. Here are some of the biggest hurdles:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, pandemics, and political instability can disrupt commodity chains, causing delays and shortages.
- Sustainability Concerns: As environmental awareness grows, there’s increasing pressure on businesses to adopt sustainable practices throughout their commodity chains.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex web of international regulations can be a daunting task for companies operating in global markets.
To overcome these challenges, businesses must adopt innovative solutions and collaborate with stakeholders across the chain. This could involve investing in new technologies, implementing sustainable practices, or forming strategic partnerships with suppliers and distributors.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Commodity Chains
Let’s take a look at some real-world examples of commodity chains to see how they work in practice.
1. Coffee Commodity Chain
From bean to cup, the coffee commodity chain involves farmers, processors, roasters, and retailers. Coffee beans are grown in countries like Brazil and Colombia, processed and roasted, and then distributed to cafes and grocery stores worldwide. This chain is a prime example of how global trade connects producers and consumers across continents.
2. Smartphone Commodity Chain
The smartphone commodity chain is a marvel of modern engineering. It involves chip manufacturers, assembly plants, logistics companies, and retailers. Each component of a smartphone, from the screen to the battery, is sourced from different parts of the world and assembled into the final product. This chain highlights the complexity and interdependence of global manufacturing networks.
The Future of Commodity Chains
As the world continues to evolve, so too will commodity chains. Emerging trends like automation, digitization, and sustainability will shape the future of these chains, making them more efficient, transparent, and environmentally friendly. Businesses that adapt to these changes will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.
For example, the rise of e-commerce has transformed how goods are distributed, with companies like Amazon and Alibaba revolutionizing the retail landscape. Meanwhile, the push for sustainability is driving companies to adopt circular economy models, where waste is minimized, and resources are reused.
Opportunities for Innovation
Commodity chains offer countless opportunities for innovation. From developing new materials and processes to leveraging cutting-edge technologies, businesses can find ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences. By embracing innovation, companies can stay ahead of the curve and meet the evolving needs of consumers and stakeholders.
How to Optimize Your Commodity Chain
If you’re a business owner or manager, optimizing your commodity chain can lead to significant benefits. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Map Your Chain: Identify all the players and processes involved in your chain to gain a clear understanding of its structure and dynamics.
- Invest in Technology: Adopt technologies like IoT and AI to improve visibility, efficiency, and decision-making.
- Focus on Sustainability: Implement sustainable practices to reduce your environmental impact and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
By taking these steps, you can enhance the performance of your commodity chain and gain a competitive edge in your industry.
Conclusion: Why Commodity Chains Matter
In conclusion, commodity chains are the backbone of global trade and economy. They connect producers, suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers, enabling the flow of goods and services across the world. Understanding how these chains work is essential for anyone interested in economics, business, or global affairs.
So, whether you’re a business owner looking to optimize your operations or a consumer curious about where your products come from, this article has hopefully provided you with valuable insights into the world of commodity chains. Now, it’s your turn to take action—leave a comment, share this article, or explore our other content to learn more about the fascinating world of global trade.
Table of Contents:
- What Exactly is a Commodity Chain?
- The Key Players in a Commodity Chain
- Types of Commodity Chains
- How Commodity Chains Impact Global Trade
- The Role of Technology in Commodity Chains
- Challenges Facing Commodity Chains
- Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Commodity Chains
- The Future of Commodity Chains
- Opportunities for Innovation
- How to Optimize Your Commodity Chain