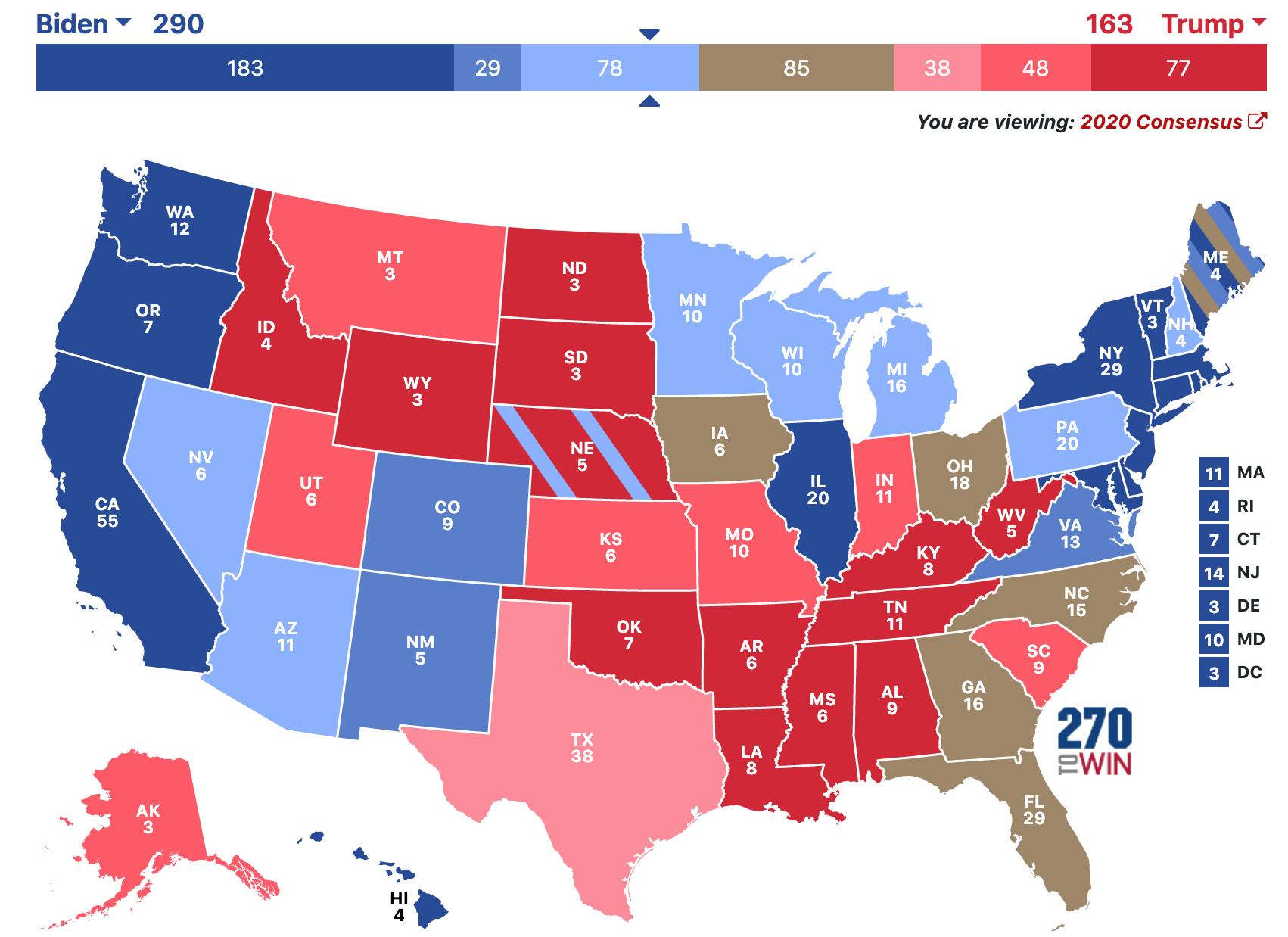
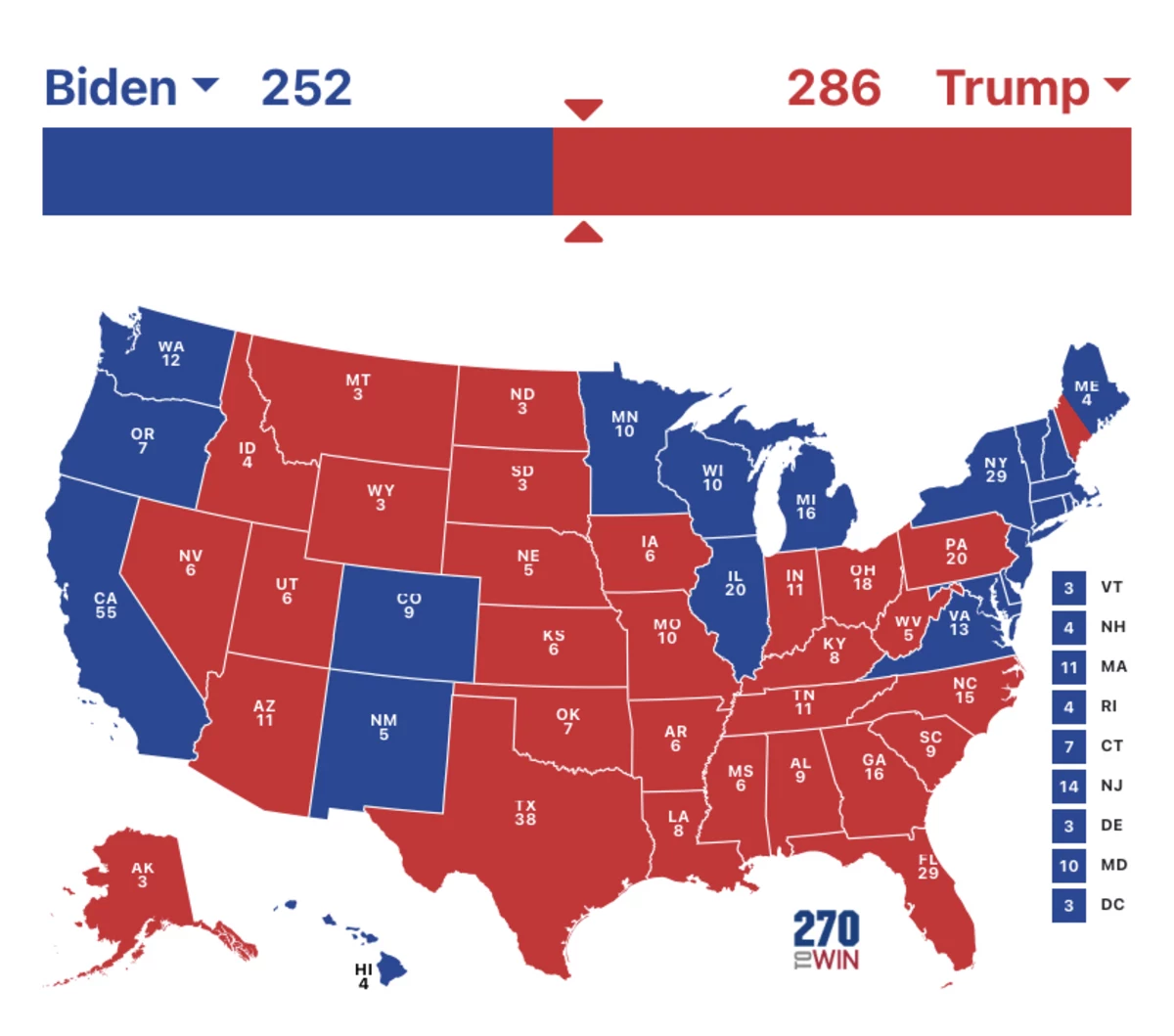
Let’s talk about the is electoral map because it’s a topic that affects every single one of us, whether we realize it or not. Picture this: election night, the screen filled with red and blue states, and everyone waiting anxiously for the results. But what exactly is an electoral map? It’s more than just colors on a screen; it’s a powerful tool that shapes how our democracy works. From deciding who becomes president to influencing policy decisions, understanding this map can give you an edge in navigating today's political landscape.
Now, before we dive deep into the nitty-gritty, let me ask you something. Have you ever wondered why some states seem to matter more than others during elections? Or why candidates spend so much time campaigning in places like Florida but barely visit others? That’s where the is electoral map comes into play. It’s like a blueprint for winning—or losing—an election.
So, buckle up because we’re about to break down everything you need to know about the is electoral map. From its history to its impact on modern politics, we’ll cover it all. By the end of this guide, you’ll not only understand how it works but also how it affects your life. Sound good? Let’s get started!
Read also:Elon Musk And The Transphobic Debate Unpacking The Controversy
What Exactly Is an Electoral Map?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. An electoral map is essentially a visual representation of how votes are distributed across different regions in a country during an election. In the U.S., it specifically refers to the map that shows which states have cast their electoral votes for each presidential candidate. Each state is assigned a certain number of electoral votes based on its population, and these votes ultimately determine who wins the presidency.
Think of it like a giant game of chess. Candidates strategize by focusing on states with the most electoral votes because those are the ones that can make or break their chances of victory. And guess what? This system has been around since the founding of the nation, though it’s evolved quite a bit over the years.
How Does the Electoral Map Work?
Here’s the deal: when you cast your vote in a presidential election, you’re not directly voting for the candidate. Instead, you’re voting for a group of people called electors who then cast their votes on behalf of the state. The number of electors a state gets equals the total number of its representatives in Congress—both House members and Senators.
- There are 538 electoral votes in total.
- A candidate needs at least 270 electoral votes to win the presidency.
- Most states operate under a winner-takes-all system, meaning the candidate who wins the popular vote in that state gets all of its electoral votes.
It’s a fascinating system, right? But it’s also one that’s been the subject of debate for years. Some people argue that it’s outdated and doesn’t truly reflect the will of the people, while others believe it’s essential for balancing power between large and small states.
The History Behind the Is Electoral Map
Let’s take a trip back in time to understand how the electoral map came to be. When the Founding Fathers were drafting the Constitution, they faced a big challenge: how to ensure that smaller states weren’t overshadowed by larger ones in presidential elections. Their solution? The Electoral College, which eventually gave rise to the electoral map we know today.
In the early days, the system was pretty straightforward. Each state would choose its electors, and those electors would cast their votes for president. Over time, however, things got more complicated. For example, the rise of political parties changed how electors were chosen, and the introduction of the popular vote added another layer to the process.
Read also:Whats Aocs Net Worth Unpacking The Financials Of Alexandria Ocasiocortez
Key Moments in Electoral Map History
- 1824 Election: The first time a candidate won the popular vote but lost the presidency due to the electoral map.
- 2000 Election: A modern example of the same phenomenon, where George W. Bush won the presidency despite losing the popular vote to Al Gore.
- 2016 Election: Another controversial case where Donald Trump won the presidency despite receiving fewer votes than Hillary Clinton nationwide.
These moments highlight both the strengths and weaknesses of the electoral map system. While it ensures that smaller states have a voice, it can sometimes feel out of sync with the will of the majority. It’s a balancing act that continues to spark heated debates.
Why Does the Is Electoral Map Matter?
Here’s the million-dollar question: why should you care about the electoral map? Well, for starters, it determines who becomes president of the United States. But beyond that, it also influences how candidates campaign and where they focus their efforts. Swing states—those that could go either way—are particularly important because they often hold the key to victory.
For example, in recent elections, states like Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin have become battlegrounds because their electoral votes can swing the outcome. This means that candidates pour resources into these areas, hoping to win over undecided voters. Meanwhile, states that consistently vote for one party or the other—like California for Democrats or Texas for Republicans—often get less attention.
Impact on Voter Turnout
Another interesting aspect of the electoral map is its effect on voter turnout. In states where the outcome is a foregone conclusion, some people may feel like their vote doesn’t matter as much. On the other hand, in swing states, the stakes are much higher, and voters are more likely to turn out in droves.
This disparity can lead to uneven participation rates across the country, which raises important questions about fairness and representation. Should every vote really count equally, or is the current system the best we can do?
How to Read and Analyze the Is Electoral Map
Now that you know what the electoral map is and why it matters, let’s talk about how to read it. At first glance, it might seem like just a bunch of colors on a screen, but there’s actually a lot of information packed into that map.
Red typically represents Republican-leaning states, while blue represents Democratic-leaning states. Purple or gray might indicate swing states or states where the outcome is still uncertain. By looking at the map, you can get a sense of which candidate has the upper hand and where the race is likely to be decided.
Tips for Analyzing the Map
- Look at the number of electoral votes each state has and how they’re distributed.
- Pay attention to swing states and key battleground areas.
- Consider historical trends and how they might influence the current election.
Reading the map is like solving a puzzle. The more you know about the pieces, the better you’ll be able to predict the outcome. And let’s be honest, who doesn’t love a good mystery?
Common Misconceptions About the Is Electoral Map
Before we move on, let’s clear up some common misconceptions about the electoral map. For one, it’s not just a random collection of colors. There’s a method to the madness, and understanding it can help you make sense of election results.
Another misconception is that the popular vote doesn’t matter at all. While it’s true that the electoral map determines the winner, the popular vote still plays a role in shaping public opinion and influencing future elections. Plus, it’s a key indicator of the nation’s mood and priorities.
Myth vs. Reality
- Myth: The electoral map always reflects the will of the people.
- Reality: Sometimes it doesn’t, which is why debates about reforming the system continue.
- Myth: Smaller states don’t have any power in presidential elections.
- Reality: The electoral map ensures that even small states have a voice in the process.
Understanding these nuances can help you separate fact from fiction and become a more informed voter.
Future of the Is Electoral Map
So, where is the electoral map headed in the future? That’s a question that’s up for debate. Some advocates are pushing for reforms, like adopting a national popular vote system, while others believe the current system should stay intact.
Whatever happens, one thing is certain: the electoral map will continue to play a crucial role in shaping American democracy. As the country grows and changes, so too will the map and the strategies candidates use to win it.
Potential Reforms
- National Popular Vote Interstate Compact: An agreement among states to award their electoral votes to the candidate who wins the national popular vote.
- Proportional Allocation: Dividing electoral votes based on the percentage of the popular vote each candidate receives.
These ideas are still in the early stages, but they could have a big impact on how future elections are conducted. Only time will tell which direction we’ll go.
Conclusion: Your Role in Shaping the Electoral Map
Well, there you have it—the ultimate guide to understanding the is electoral map. From its history to its impact on modern politics, we’ve covered it all. But here’s the thing: the map doesn’t just shape elections—it’s shaped by the people who participate in them. That includes you.
So, what can you do? First, stay informed. Keep up with the latest news and trends, and don’t be afraid to ask questions. Second, get involved. Whether it’s volunteering for a campaign or simply encouraging others to vote, every action counts. Finally, remember that your voice matters. Even if the electoral map seems complex, your vote can make a difference.
Now, it’s your turn. Share this article with your friends, leave a comment below, or check out some of our other guides on related topics. Together, we can create a more informed and engaged electorate. And isn’t that what democracy is all about?
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is an Electoral Map?
- How Does the Electoral Map Work?
- The History Behind the Is Electoral Map
- Key Moments in Electoral Map History
- Why Does the Is Electoral Map Matter?
- Impact on Voter Turnout
- How to Read and Analyze the Is Electoral Map
- Tips for Analyzing the Map
- Common Misconceptions About the Is Electoral Map
- Myth vs. Reality
- Future of the Is Electoral Map
- Potential Reforms